Introduction
In recent years, blockchain technology has taken the world by storm. From cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to digital contracts and secure data sharing, blockchain is changing the way we interact with technology. But what exactly is blockchain, and how does it work?
This blog explains blockchain technology in simple terms, perfect for beginners and curious minds who want to understand the basics without getting lost in technical jargon.
What is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, blockchain is a digital ledger—a way to record transactions and information securely, transparently, and in a way that cannot be changed.
Imagine a notebook that everyone can see, no one can erase, and new pages can only be added—not edited or deleted. That’s essentially what a blockchain is.
Each page in this notebook is called a block, and these blocks are connected in achain—hence the name blockchain.
Key Features of Blockchain
✅ Decentralized
Unlike traditional databases controlled by one organization (like a bank), blockchain is decentralized. It is maintained by a network of computers (called nodes) around the world. No single person or company owns it.
✅Immutable
Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changedor tampered with. This creates a permanent record of every transaction.
✅ Transparent
Every transaction can be seen by all users. This creates trust and ensures that no one can cheat the system without being noticed.
✅ Secure
Blockchain uses advanced cryptography to secure data, making it nearly impossible for hackers to manipulate the information.
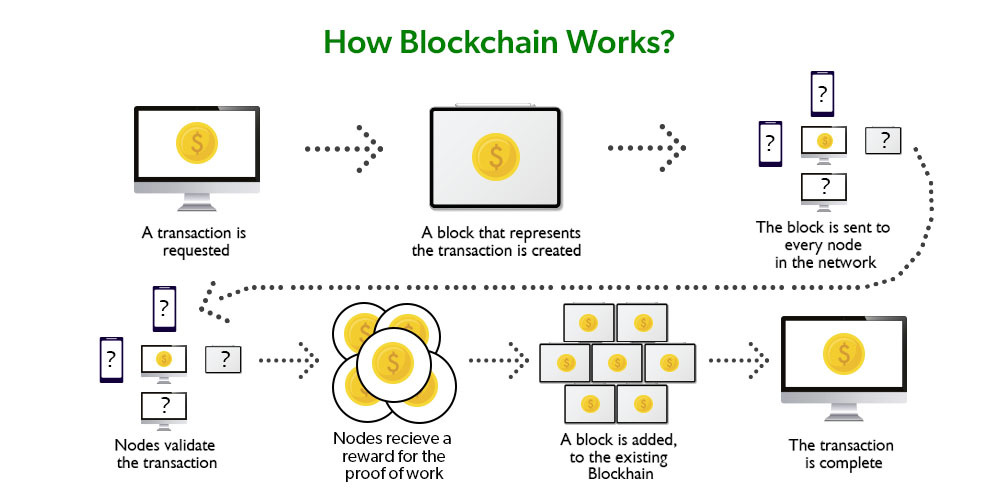
How Does Blockchain Work? Step-by-Step
Let’s break it down into simple steps:
🔹 Step 1: A Transaction is Requested
Someone wants to send money, create a contract, or record any other type of data.
🔹 Step 2: The Transaction is Broadcast
This transaction is sent to a network of computers (nodes) around the world.
🔹 Step 3: Verification
These nodes use algorithms to check if the transaction is valid. For example, does the person have enough money to send?
🔹 Step 4: Block Creation
Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others to form a block.
🔹 Step 5: Block is Added to the Chain
The block is then added to the existing blockchain. This chain grows over time, creating a full history of transactions.
🔹 Step 6: Transaction is Complete
The process is complete. The user is notified, and the transaction is now part of the blockchain forever.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain
💰 Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies use blockchain to manage and record transactions without needing a bank.
📄 Smart Contracts
Blockchain can automate contracts so they execute when conditions are met—without needing lawyers or middlemen.
🛒 Supply Chain
Companies use blockchain to track products from the factory to the customer, ensuring quality and transparency.
📁 Healthcare
Patient records can be securely shared among doctors using blockchain, reducing errors and delays.
Benefits of Blockchain
-
🔐 More secure than traditional systems
-
⚡ Faster and more efficient than manual processes
-
📜 Creates a permanent and reliable record
-
💵 Reduces need for third-party verification
-
🌍 Can be used globallywithout borders
Challenges of Blockchain
-
🧠 Steep learning curve
-
🖥️ Requires significant computing power
-
🔋 Some blockchains (like Bitcoin) use a lot of energy
-
📉 Not yet widely adopted in some industries
Future of Blockchain
Blockchain is still evolving. Experts believe it will soon power:
-
Digital identity systems
-
Voting systems
-
Decentralized finance (DeFi)
-
Secure file storage
-
Even the Metaverse and NFTs
Internal Linking (Suggested Topics for Future Blogs)
To dive deeper into blockchain, check out our upcoming posts:
Conclusion
Blockchain technology might sound complicated at first, but at its heart, it's just a smart way to store and secure information. As this technology becomes more common, understanding its basics will be a valuable skill for anyone interested in the future of digital transactions, security, and innovation.
Stay tuned for more beginner-friendly tech blogs!